HTTPS is a network security transmission protocol. The URL starts with https://, which means that this protocol is used. Apple’s latest mobile operating system, iOS 9, not only brings many new features, but also improves the security of the entire system, as [iOS developer resources](https://developer.apple.com/library/ prerelease/ios/releasenotes/General/WhatsNewIniOS/Articles/iOS9.html) says
If you’re developing a new app, you should use HTTPS exclusively. If you have an existing app, you should use HTTPS as much as you can right now, and create a plan for migrating the rest of your app as soon as possible . In addition, your communication through higher-level APIs needs to be encrypted using TLS version 1.2 with forward secrecy. If you try to make a connection that doesn’t follow this requirement, an error is thrown.
That’s right, starting with iOS 9, non-HTTPS requests will be gradually disabled! Even existing programs will still work in iOS 9 without HTTPS. But I believe that in the near future, all programs will use HTTPS, and HTTP will be completely eliminated. So why use HTTPS? What about using HTTPS in those cases?
Reasons to Use HTTPS
HTTPS can encrypt data transmission, preventing man-in-the-middle interception or modification. Ability to encrypt user information and website content. For example, if you use what the public calls “insecure free Wi-Fi”, if all the web pages a user visits are HTTPS, then this Wi-Fi has no effect on the user. In other words, the “free Wi-Fi is not safe” reported by the media is pure rumor and has no truth. When HTTPS and HSTS are enabled, free Wi-Fi cannot intercept any information such as user passwords at all, and users can make payments and other operations with peace of mind. Obviously, CCTV 315 is lying to everyone without any professional knowledge and explanation that “free Wi-Fi is not safe”, which is completely intimidating the audience. The reason why all the photos in WeChat Moments can be obtained is because WeChat Moments uploads are in plain text, which is obviously a problem of WeChat itself, obviously not all software has such a problem. With the release of iOS 9 and the enforcement of HTTPS, this type of problem will no longer exist. Second, using HTTPS is not only to prevent information theft, but also to prevent information from being modified in the middle. For example, China Unicom and China Mobile will modify the content of the website and put their own advertisements to let users upgrade their products, but these advertisements are not prepared by the website owner, and the website owner does not know it in advance. Although they have no ethical bottom line in doing so, we only need to use HTTPS, and there is nothing these operators can do. The “404 error page optimization” of Xiaomi routers also uses the same principle to tamper with non-HTTPS pages and provide users with their own advertisements for profit. It is hijacking in itself, no exaggeration. In addition, some users also found that even on normal pages, there are advertisements added by Xiaomi through hijacking web page code injection. But when HTTPS becomes commonplace, all of this will disappear. However, before HTTPS became popular, some website owners who did not support HTTPS could only endure being hijacked by operators and routers.
Where to Use HTTPS
In my opinion, it is necessary for all web pages and programs to use HTTPS in full and mandatory to avoid the above situation. Including personal websites, HTTPS should also be fully enabled to prevent the loss of readers due to tampered and implanted advertisements. Using HTTPS doesn’t add much cost and can make pages faster. The SPDY protocol can minimize network delay, improve network speed, and optimize the user’s network experience. However, the SPDY protocol only supports HTTPS. With the current trend, more and more webmasters will actively or forced to use HTTPS, and HTTPS is about to become mainstream. China is the country with the least popularity of HTTPS, but with Baidu’s full-site HTTPS and UPYUN’s support for HTTPS with custom domain names, it will promote the development of HTTPS in the entire industry.
Advantages of Using HTTPS
Encrypted Transmission
If a web page does not use HTTPS, it means that the content on the page, the keywords you are searching for, and even the username and password are not encrypted, and “middlemen” can read and tamper with these unencrypted content. For example, the free Wi-Fi you connect to, the operator, etc. may modify the content of the web page. These middlemen will add their ads on web pages, modify 404 page styles, and read pictures in your WeChat Moments without your permission. But when HTTPS is enabled on this web page, the data on the page will be encrypted. Under normal circumstances, the man-in-the-middle cannot obtain your data, but if the man-in-the-middle replaces the original HTTPS, the attack is still possible, so the HTTPS site A certificate must be included for verification.
Verify
Since HTTPS sites must include a certificate for authentication, it is possible to verify that the server is licensed by the domain owner (to prevent connections to man-in-the-middle servers). Usually browsers will verify this certificate, and if the certificate is wrong it will warn the user that there is a problem with the website they are visiting. If the user’s DNS service is polluted, it is possible to forge the identity to another host (IP address), which is even more terrible than a man-in-the-middle attack and can do more. When a user accesses using HTTPS, the browser will verify the certificate of the website, and if the certificate is wrong, it will warn or even fail to access. But if the user access is using HTTP, then the server will not be authenticated. Full authentication is only possible if the website enforces HTTPS (that is, disables HTTP links) and has HSTS enabled. Once HSTS is enabled, all pages of this domain name can only be accessed via HTTPS within the set validity period.
Encryption Tips
For pages where all resources under the site use the HTTPS protocol, many browsers will have encryption prompts to inform users that the site is encrypted, making the entire site higher. However, I would like to remind users that not all pages using HTTPS are safe, and any website can easily apply for an SSL certificate, so it is still necessary to identify the domain name itself. However, it is more trustworthy for HTTPS sites that directly display their company name, because this kind of certificate needs to be verified by paper proof materials. Below are the encryption prompts for accessing some HTTPS sites using Chrome for Mac. Chrome’s encryption prompt menu is divided into two parts, the first part is verification, and the latter part is encryption, which can usually be divided into the following four types:
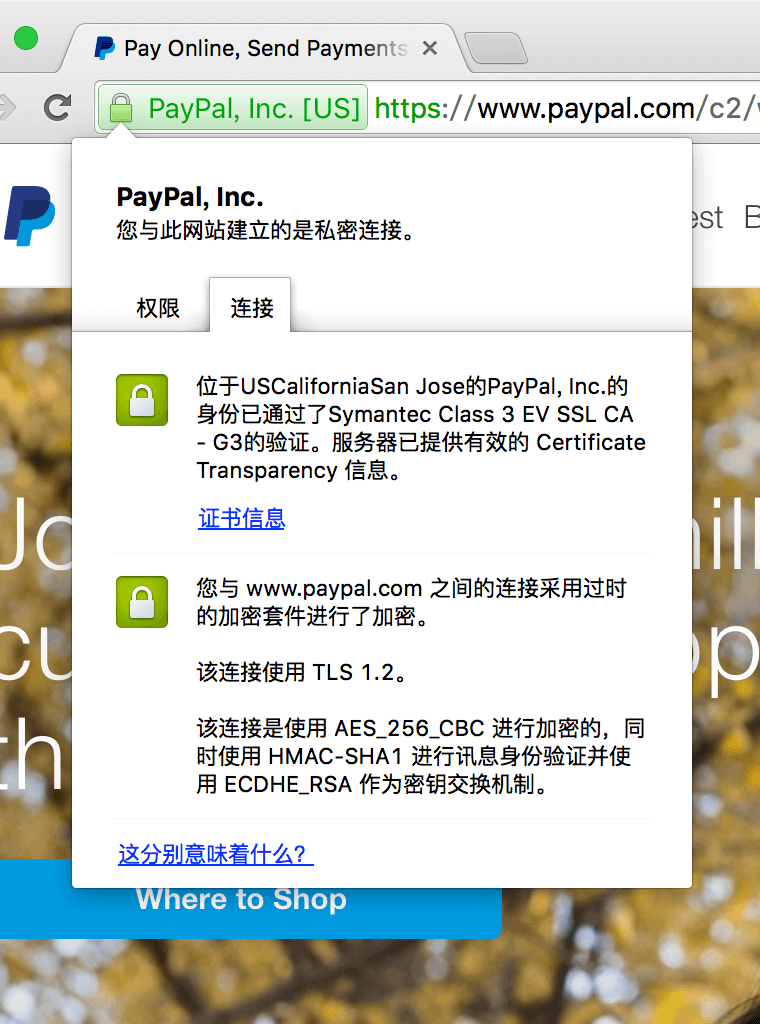
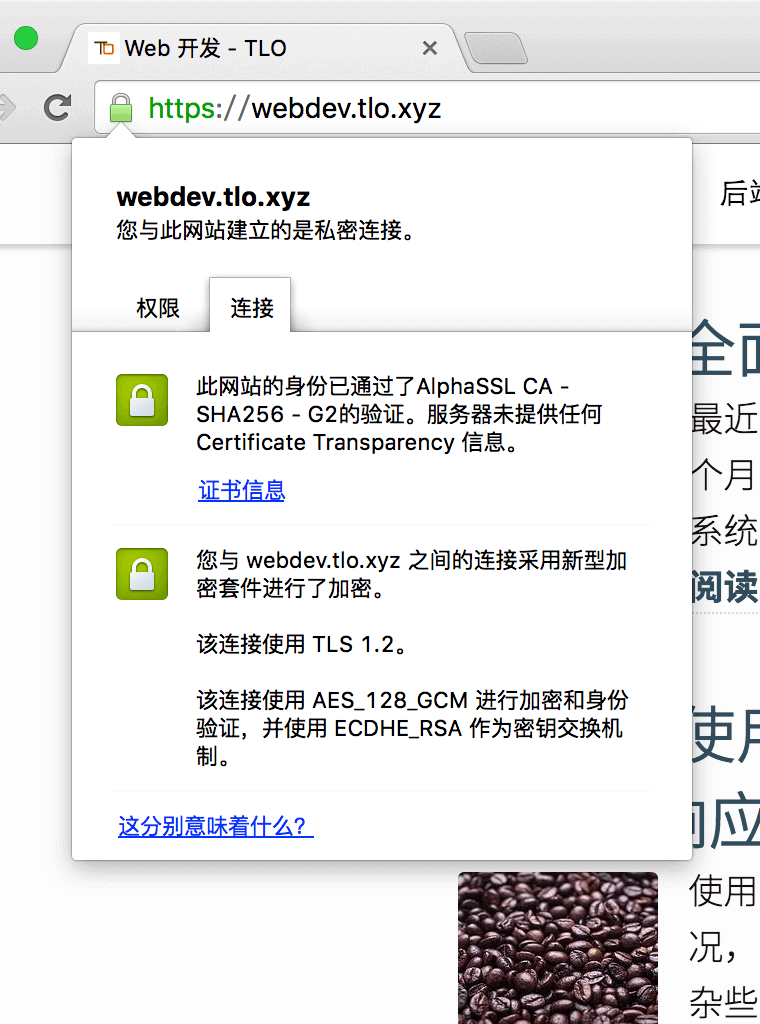
The first and second cases represent that a sufficiently secure encryption method is used (but the second one does not provide any Certificate Transparency information), but the signature level of the certificate is different, which has nothing to do with the encryption method and the security of the verification. In any case, it can be guaranteed that the certificate is not forged.
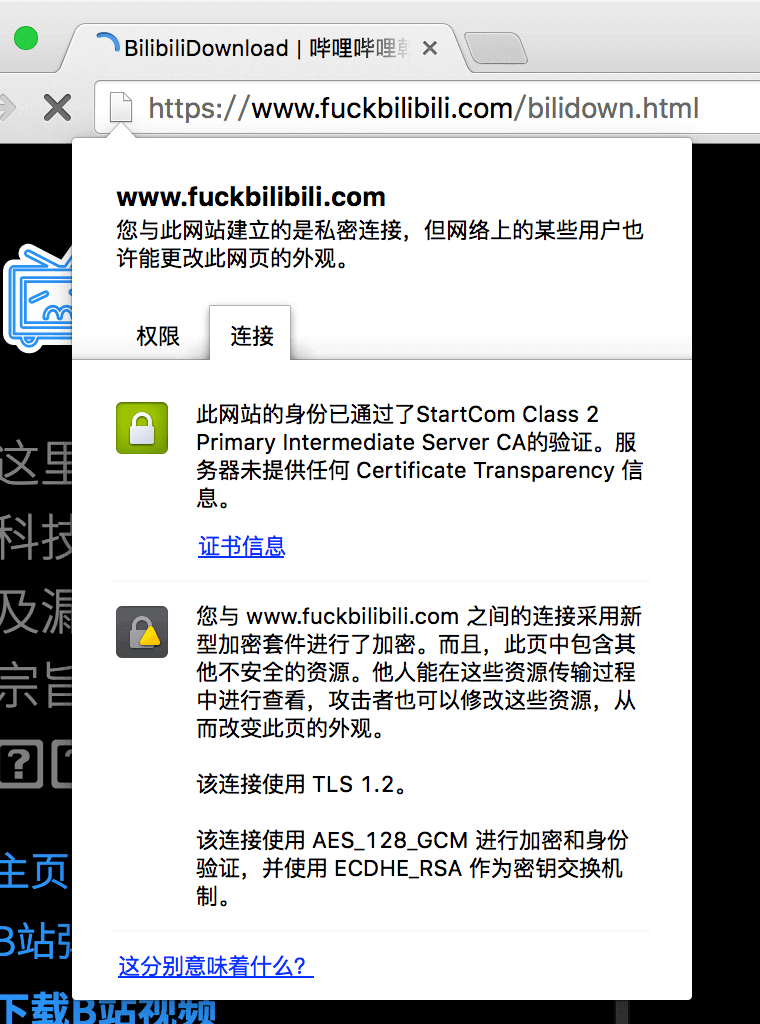
The third case is containing unsafe resources, the appearance of the website may be changed, but the HTML text itself is reliable.
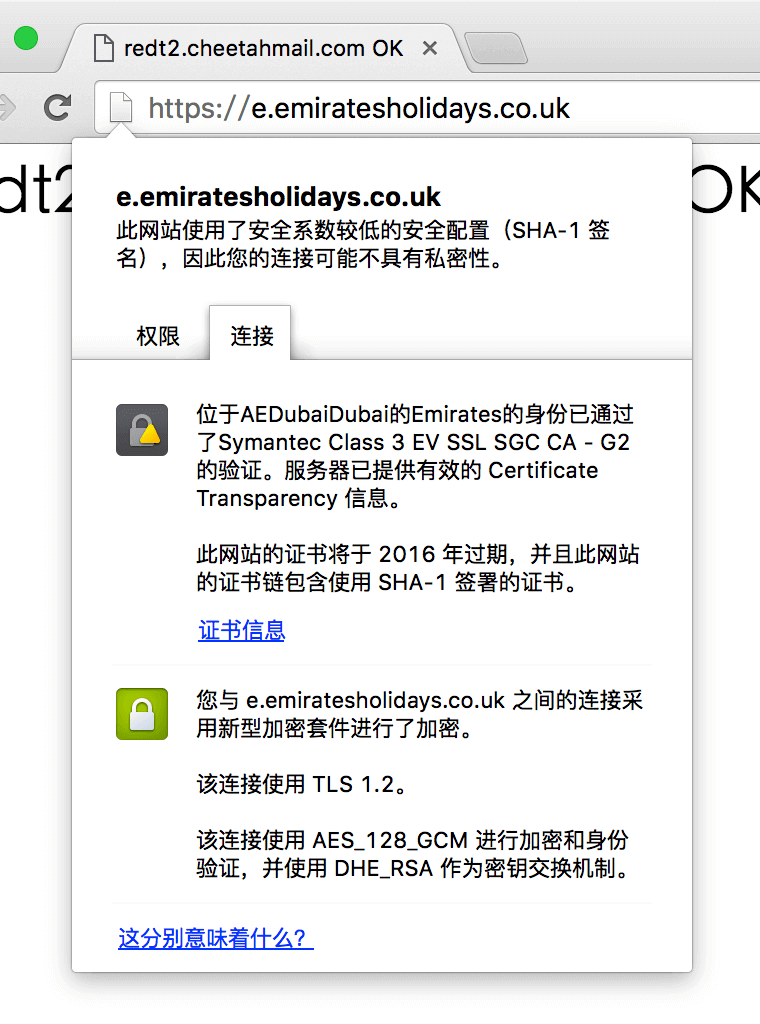
The fourth case is a certificate signed with SHA-1. Since SHA-1 is not secure enough, that is to say, the security of verification is not enough. Since the cost of forging such a certificate is getting lower and lower, it may not be secure. Encryption for such a site is still adequate.
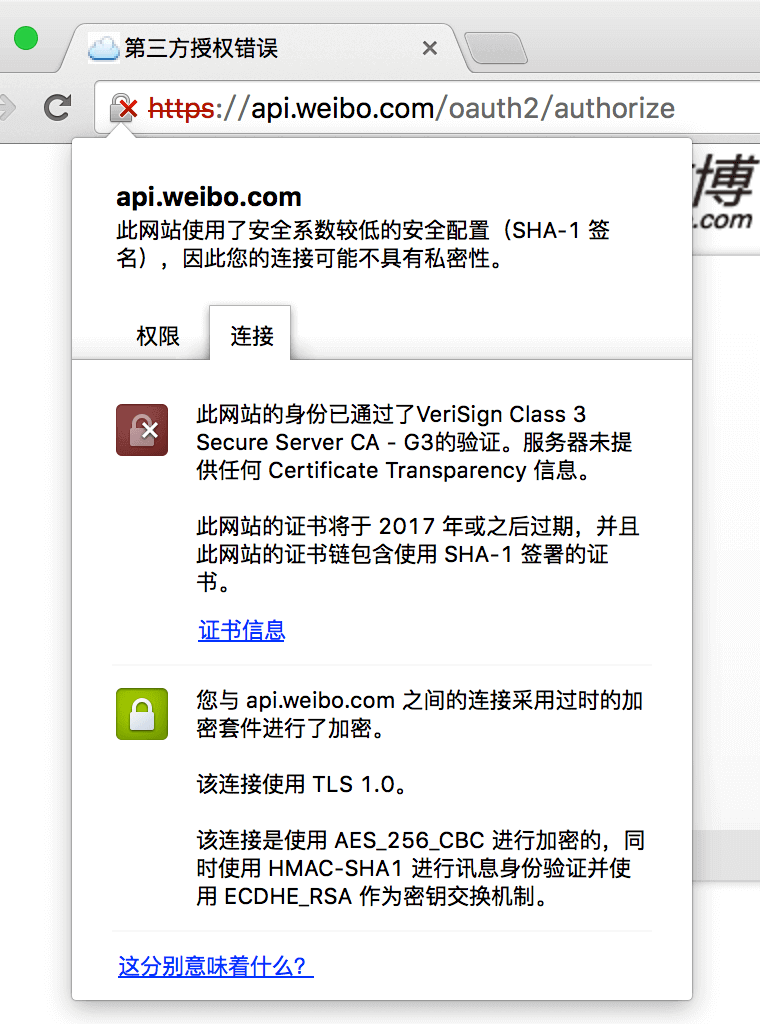
The fifth case represents a possible man-in-the-middle attack (since no Certificate Transparency information is provided, and SHA-1 is used).
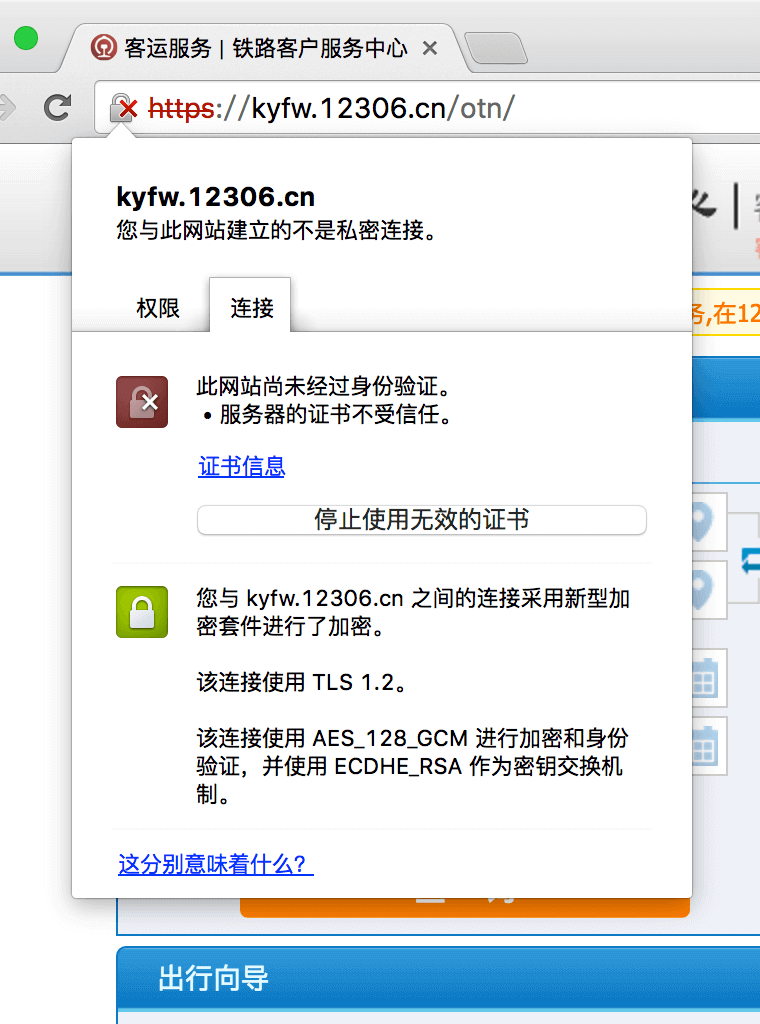
The sixth case means that the website uses a certificate issued by an untrusted root certificate (or the certificate does not contain the current domain name). Encryption tips for Chrome In any case, I do not recommend you to use SHA-1 signed certificates, it is worth noting that the latest version of Safari can also choose SHA-1 signed certificates are not trusted anymore, SHA-1 is about to become obsolete.
Search Engine
Google’s crawling of HTTPS sites is very friendly, and officials say that using HTTPS will also improve rankings. Google also supports HTTPS sites using the SNI protocol. Baidu has recently supported the crawling of HTTPS sites and will increase the ranking accordingly. After testing, not all certificates are supported, but the SNI protocol is also supported.
Disadvantages of Using HTTPS
Slower Loading Speed
It has to be said that using HTTPS does increase the delay. This delay is mainly reflected in the loading of the first page, and entering the next page will be much faster. In my test, there will be 2~5 times more delay after enabling HTTPS. If there are resources in other domains, then these resources will also have so much more delay.
Compatibility Issues
The SNI protocol has been widely used, but there are still some devices that are not compatible, such as Windows XP’s IE8 and previous browsers are not compatible. As of now, the usage rate of browsers supporting SNI in China has reached 95%.
Search Engine
Some search engines are fine with HTTPS, but others don’t support it. However, more and more search engines are gradually supporting HTTPS, I don’t think there is any need to worry.
Cost
A certificate is required to use HTTPS. Now that there are more and more free SSL certificates, the cost of implementing HTTPS in general is getting lower and lower. However, as the cost of certificate issuance is getting lower and lower, the function of HTTPS as verification will become smaller, but the function of encryption will still exist.
Other
HTTPS can only prevent tampering to a certain extent, but it cannot resist some powerful [network blocking](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E9%98%B2%E7%81%AB%E9%95 %BF%E5%9F%8E). At present, some “rogue” browsers do not verify certificates, which greatly weakens security. If the certificate is not verified, there is still encryption, but if the DNS is polluted, a man-in-the-middle attack is still feasible. If the DNS is polluted, but HTTPS is still required, the site will not be accessible. So DNS is also in great need of encryption. If DNSSEC or “HTTPS DNS” (that is, using the HTTPS protocol to resolve DNS) can be supported as soon as possible, then HTTPS as a verification will not be so important, and the day when there is no man-in-the-middle attack at all is just around the corner (but it is still impossible without network blocking). Perhaps future browsers can only access HTTPS sites, just like iOS 9 vigorously promotes HTTPS, which can greatly improve security and resist man-in-the-middle attacks.
Force HTTPS with .htaccess
The following is the configuration in .htaccess in Apache
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP:X-Forwarded-Proto}=http
RewriteRule ^ https://%{HTTP\_HOST}%{REQUEST\_URI} \[L,R=301\] # disable HTTP protocol
HSTS and HSTS Preload List
HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security, HTTP Strict Transport Security) is a way to make browsers enforce HTTPS. When a user visits an HTTPS site, the server returns a Header, informing the browser that HTTPS must be enforced under this domain name, within the validity period , the browser will only use HTTPS to access this domain name. The following is the configuration in .htaccess in Apache.
Header set Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=315360000; preload; includeSubDomains" env=HTTPS
For example, when visiting http://tlo.xyz for the first time, the browser will be redirected to https://tlo.xyz by 301, and then it will receive this Header. Within 10 years, all files under tlo.xyz will be All domain names will only use HTTPS, including the second-level domain name ze3kr.tlo.xyz. But this is not over yet. If the website has been hijacked by HTTPS when the browser is accessed for the first time, then it is meaningless to do so, so you need to include the preload parameter after starting HSTS, and then go to Submit, pay attention to the requirements. After you submit it, you will be able to see your domain name in the source code of major browsers after a period of time.
Check your SSL configuration
Go to SSL Server Test to give your server’s SSL configuration a score. oh, the difference
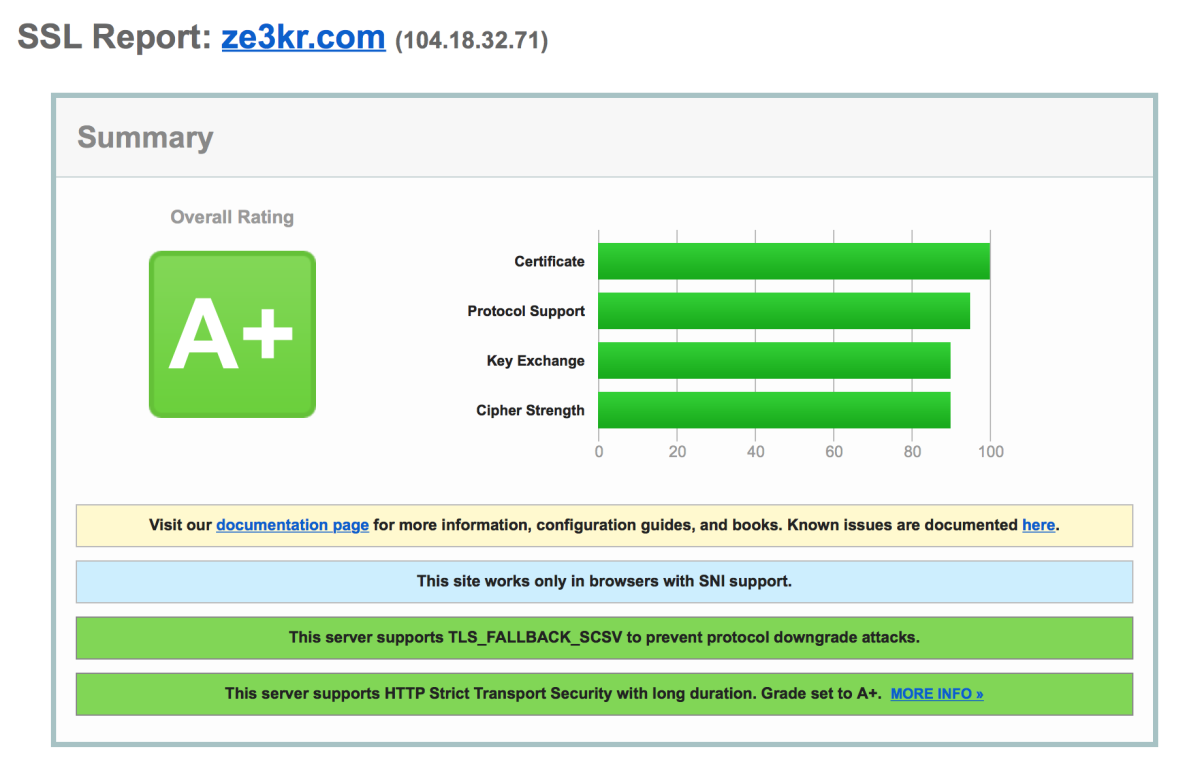
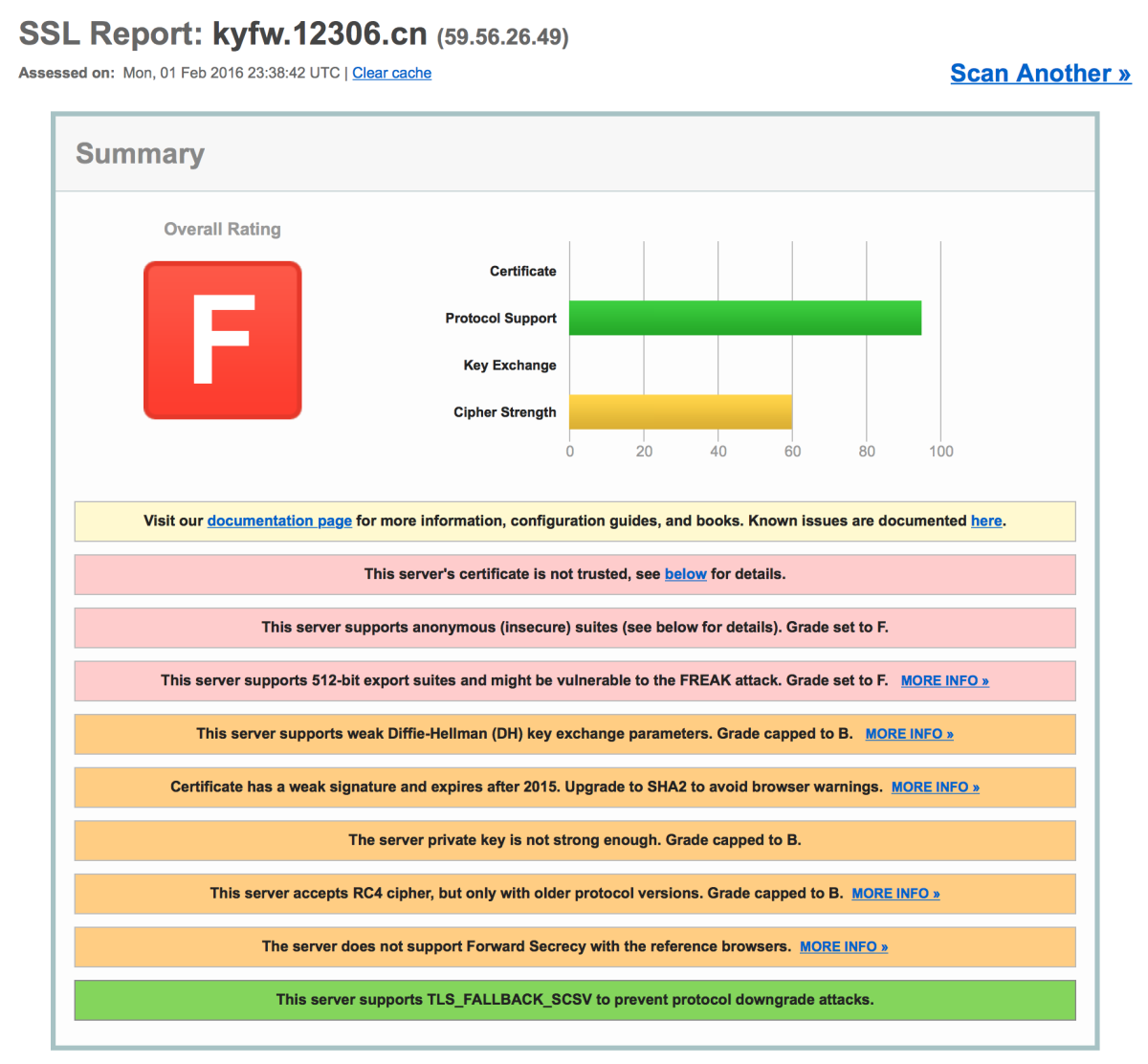
Tips
- Once the mandatory HTTPS protocol is set or HSTS is enabled, it is difficult to return to the HTTP protocol (especially the latter). If the HTTPS protocol is suddenly turned off, users may not be able to access the website for a long time, or the certificate may report an error, resulting in a large loss user. So think carefully before deciding to force HTTPS.